Which Muscles Would a Baby Gain Voluntary Control Over First During Development?
Fetal development
Zygote; Blastocyst; Embryo; Fetus
Learn how your baby is conceived and how your baby develops inside the mother's womb.
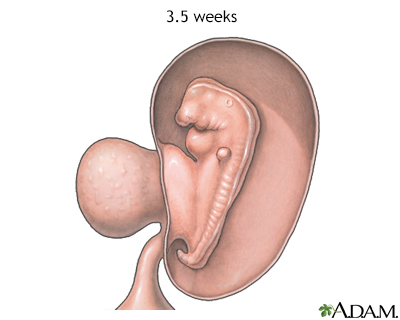
At 3.five weeks, the fetus will have formed the heart, begins development of the brain and spinal string, and starts forming the gastrointestinal tract.
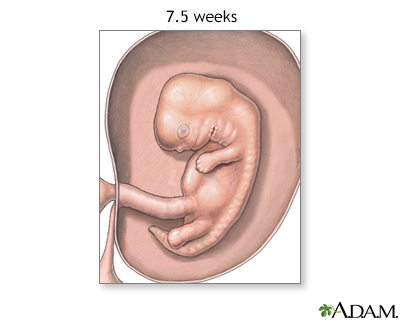
At 7.5 weeks, the eyes motion forrad on the confront and eyelids brainstorm to form, the palate is nearing completion and the natural language begins to form, the alimentary canal separates from the genitourinary tract, and all essential organs accept begun to grade.
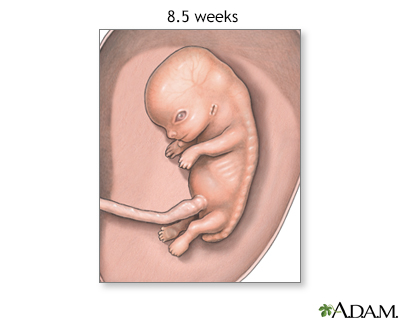
At eight.5 weeks, the embryo at present resembles a human. Facial features go on to develop, the beginnings of external genitalia form, the anal passage opens although the rectal membrane is intact, apportionment through the umbilical string is well adult, and long bones begin to grade.
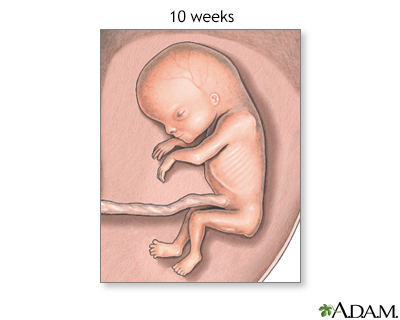
A fetus at 10 weeks of evolution has fully formed eyelids and well-formed digits and ears.
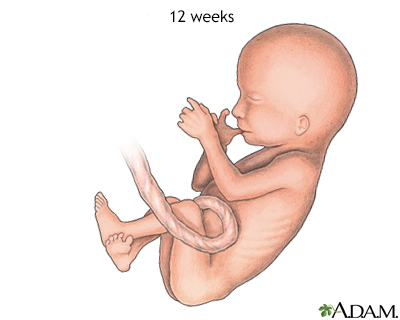
A fetus at 12 weeks tin can make a fist and suck its pollex.
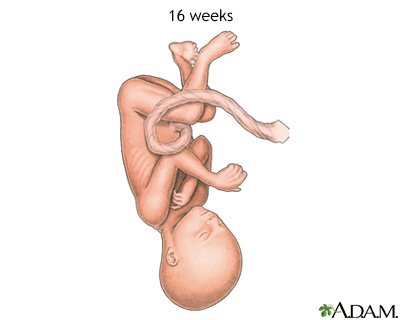
At week 16, the fetus reaches a length of about 6 inches, makes active movements, and makes sucking motions with the rima oris.
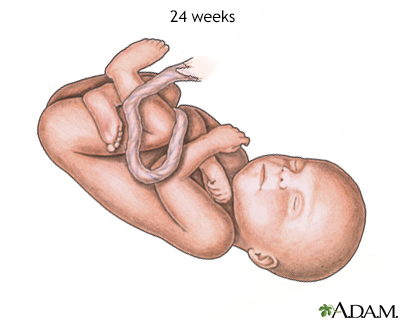
At 24 weeks, the fetus has fully adult optics, has a mitt and startle reflex, is forming footprints and fingerprints, and is forming alveoli in the lungs.
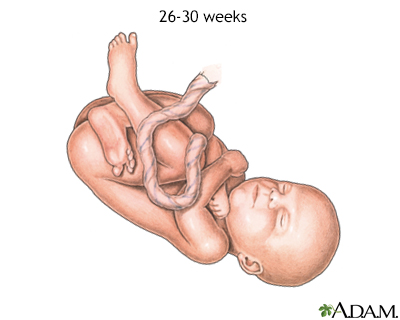
At 26 to 30 weeks, a fetus is speedily developing its brain controls and some torso functions. The fetus has eyelids which open up and close and has a speedily developing respiratory organisation.
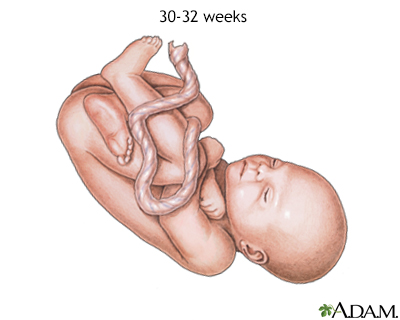
At 30 to 32 weeks, a fetus has increased cardinal nervous system control over trunk functions and rhythmic breathing movements. It is still developing lungs and is partially in control of body temperature.
Information
WEEK By WEEK CHANGES
Gestation is the period of time between conception and birth when a baby grows and develops within the female parent's womb. Because it's impossible to know exactly when conception occurs, gestational age is measured from the showtime twenty-four hours of the mother's last menstrual bike to the electric current date. It is measured in weeks.
This means that during weeks 1 and two of pregnancy, a woman is non yet pregnant. This is when your body is preparing for a infant. A normal gestation lasts anywhere from 37 to 42 weeks.
Week 1 to ii
- The kickoff week of pregnancy starts with the first day of a adult female'south menstrual menstruum. She is not however pregnant.
- During the stop of the second calendar week, an egg is released from an ovary. This is when you are virtually likely to excogitate if you lot have unprotected intercourse.
Week 3
- During intercourse, sperm enters the vagina after the human being ejaculates. The strongest sperm will travel through the neck (the opening of the womb, or uterus), and into the fallopian tubes.
- A single sperm and the mother's egg jail cell meet in the fallopian tube. When the single sperm enters the egg, conception occurs. The combined sperm and egg is called a zygote.
- The zygote contains all of the genetic information (Deoxyribonucleic acid) needed to get a baby. Half the Dna comes from the female parent's egg and half from the father'southward sperm.
- The zygote spends the next few days traveling down the fallopian tube. During this time, it divides to form a ball of cells called a blastocyst.
- A blastocyst is made up of an inner group of cells with an outer shell.
- The inner grouping of cells will become the embryo. The embryo is what will develop into your infant.
- The outer group of cells will go structures, chosen membranes, which nourish and protect the embryo.
Week 4
- Once the blastocyst reaches the uterus, it buries itself in the uterine wall.
- At this point in the mother'due south menstrual bicycle, the lining of the uterus is thick with blood and prepare to support a infant.
- The blastocyst sticks tightly to the wall of the uterus and receives nourishment from the mother'due south blood.
Week 5
- Week 5 is the start of the "embryonic catamenia." This is when all the baby's major systems and structures develop.
- The embryo's cells multiply and start to have on specific functions. This is called differentiation.
- Claret cells, kidney cells, and nerve cells all develop.
- The embryo grows quickly, and the infant'due south external features begin to course.
- Your baby'southward brain, spinal string, and middle begin to develop.
- Baby's gastrointestinal tract starts to form.
- Information technology is during this fourth dimension in the first trimester that the baby is most at hazard for damage from things that may cause birth defects. This includes certain medicines, illegal drug apply, heavy alcohol use, infections such as rubella, and other factors.
Weeks 6 to 7
- Arm and leg buds start to abound.
- Your baby'due south brain forms into five different areas. Some cranial nerves are visible.
- Eyes and ears brainstorm to form.
- Tissue grows that will become your infant'due south spine and other bones.
- Babe'south heart continues to grow and at present beats at a regular rhythm. This can exist seen by vaginal ultrasound.
- Blood pumps through the main vessels.
Week 8
- Baby'southward arms and legs have grown longer.
- Hands and anxiety brainstorm to form and look like little paddles.
- Your babe'due south encephalon continues to abound.
- The lungs get-go to form.
Week 9
- Nipples and hair follicles form.
- Arms grow and elbows develop.
- Babe's toes can be seen.
- All baby'south essential organs have begun to abound.
Week ten
- Your baby'due south eyelids are more developed and begin to close.
- The outer ears brainstorm to take shape.
- Baby's facial features become more than singled-out.
- The intestines rotate.
- At the end of the 10th week of pregnancy, your baby is no longer an embryo. It is now a fetus, the stage of development upwardly until birth.
Weeks 11 to xiv
- Your baby's eyelids shut and volition not reopen until nigh the 28th week.
- Baby's face is well-formed.
- Limbs are long and thin.
- Nails appear on the fingers and toes.
- Genitals appear.
- Baby's liver is making crimson claret cells.
- The head is very large -- virtually one-half of baby's size.
- Your little one tin can now make a fist.
- Molar buds appear for the baby teeth.
Weeks 15 to xviii
- At this stage, baby'southward peel is almost transparent.
- Fine hair called lanugo develops on babe'due south head.
- Muscle tissue and bones keep developing, and bones go harder.
- Infant begins to motion and stretch.
- The liver and pancreas produce secretions.
- Your little one now makes sucking motions.
Weeks 19 to 21
- Your babe tin can hear.
- The baby is more active and continues to motility and float around.
- The female parent may feel a fluttering in the lower abdomen. This is called quickening, when mom tin experience baby'south beginning movements.
- By the cease of this time, baby can eat.
Calendar week 22
- Lanugo hair covers baby's entire body.
- Meconium, baby'southward first bowel movement, is made in the intestinal tract.
- Eyebrows and lashes appear.
- The babe is more active with increased muscle development.
- The mother can feel the infant moving.
- Baby's heartbeat can exist heard with a stethoscope.
- Nails grow to the end of babe's fingers.
Weeks 23 to 25
- Os marrow begins to make claret cells.
- The lower airways of the infant'southward lungs develop.
- Your baby begins to shop fat.
Week 26
- Eyebrows and eyelashes are well-formed.
- All parts of baby'southward eyes are developed.
- Your baby may startle in response to loud noises.
- Footprints and fingerprints are forming.
- Air sacs form in baby'southward lungs, just lungs are nevertheless not prepare to work exterior the womb.
Weeks 27 to 30
- Baby's brain grows rapidly.
- The nervous system is developed enough to control some torso functions.
- Your baby's eyelids tin open and close.
- The respiratory system, while young, produces surfactant. This substance helps the air sacs fill up with air.
Weeks 31 to 34
- Your baby grows quickly and gains a lot of fat.
- Rhythmic breathing occurs, but baby's lungs are not fully mature.
- Baby'due south basic are fully developed, only are still soft.
- Your baby's body begins storing iron, calcium, and phosphorus.
Weeks 35 to 37
- Baby weighs nigh v 1/ii pounds (two.5 kilograms).
- Your infant keeps gaining weight, but will probably not get much longer.
- The skin is not every bit wrinkled as fatty forms under the skin.
- Infant has definite sleeping patterns.
- Your little one's centre and blood vessels are complete.
- Muscles and bones are fully developed.
Calendar week 38 to forty
- Lanugo is gone except for on the upper arms and shoulders.
- Fingernails may extend beyond fingertips.
- Small breast buds are present on both sexes.
- Head pilus is now coarse and thicker.
- In your 40th week of pregnancy, information technology has been 38 weeks since conception, and your infant could exist born whatever day at present.
References
Feigelman Due south, Finkelstein LH. Assessment of fetal growth and development. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 20.
Ross MG, Desai One thousand, Ervin MG. Fetal evolution, physiology, and furnishings on long-term health. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe'southward Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. eighth ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 2.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/xiii/2021
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, Doctor, Section of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. As well reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Source: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/special-topic/fetal-development
0 Response to "Which Muscles Would a Baby Gain Voluntary Control Over First During Development?"
ارسال یک نظر